
Overview
The article underscores the essential knowledge and strategies that professionals must possess to adeptly navigate the complex processes of restructuring and insolvency. It emphasises the critical importance of understanding various types of restructuring, recognising key indicators of insolvency, and comprehending the associated legal implications. Furthermore, it highlights best practices, such as:
- Early stakeholder engagement
- The need for adaptability to ensure successful outcomes amidst a shifting economic landscape.
Introduction
In an increasingly volatile economic environment, the concepts of restructuring and insolvency are critical for businesses striving to maintain their viability. Companies face mounting financial pressures; thus, understanding the nuances of these processes is essential for effective recovery and management strategies. This article delves into the fundamental aspects of restructuring, the legal frameworks governing insolvency, and the pivotal roles played by various stakeholders.
Furthermore, it highlights best practices that can enhance success rates and explores emerging trends shaping the landscape of financial recovery. By examining these elements, professionals can better navigate the complexities of restructuring and insolvency, ultimately steering their organisations toward a more sustainable future.
Understanding the Basics of Restructuring and Insolvency
The process of restructuring and insolvency represents a strategic approach aimed at reorganising an organisation’s structure, operations, or finances to enhance its viability, particularly during periods of economic distress. This proactive strategy is crucial for organisations seeking to avert bankruptcy, which is characterised as a legal condition where an entity cannot fulfil its debt obligations. A firm grasp of these concepts is essential for professionals engaged in financial recovery and management strategies.
Key elements of restructuring include:
- Types of Restructuring: There are three primary forms of restructuring:
- Operational Restructuring: This focuses on improving efficiency and effectiveness within operations, often through process optimisation and workforce adjustments.
- Financial Restructuring: This involves reorganising a company’s financial obligations, which may include renegotiating debt terms or altering capital structures to enhance liquidity.
- Organisational Restructuring: This aims to realign the company’s structure to better meet market demands, potentially involving changes in management or departmental functions.
- Indicators of Insolvency: Professionals must remain vigilant for signs of insolvency, which typically include persistent cash flow issues, an inability to meet debt payments, and declining revenues. Recognising these indicators early can facilitate timely intervention.
- Legal Implications: Transitioning from reorganisation to restructuring and insolvency can trigger legal proceedings, making it imperative for professionals to possess a solid understanding of relevant laws and regulations governing these processes.
In 2025, the UK has witnessed a notable increase in rates of restructuring and insolvency, with statistics indicating a rise of approximately 15% compared to the previous year. This trend underscores the significance of effective strategies for restructuring and insolvency. Experts assert that while restructuring and insolvency can pave the way for recovery, the prevailing economic environment suggests that merely selling assets may not address fundamental cash-flow challenges, particularly for technology firms facing diminished merger and acquisition opportunities.
Recent case studies illustrate the effectiveness of operational and economic reorganisation. For instance, numerous firms have successfully navigated economic hardship by implementing comprehensive reorganisation strategies that address both operational inefficiencies and financial commitments.
As we advance through 2025, trends in restructuring and insolvency are evolving, with an increasing emphasis on cooperative methods prioritising risk management. This shift reflects a broader understanding of the complexities involved in economic recovery, reinforcing the necessity for professionals to remain informed and adaptable in their strategies.
Navigating Legal Frameworks: Global Perspectives on Restructuring and Insolvency
Legal frameworks for restructuring and insolvency exhibit significant variation across jurisdictions, profoundly influencing how businesses manage financial distress. Key considerations include:
- Jurisdictional Variations: Each country possesses its own set of laws governing insolvency. For instance, the UK Bankruptcy Code provides a structured method for financial failure proceedings, while the UK Insolvency Act emphasises creditor protection and the systematic winding down of companies. Understanding these differences is essential for effective navigation of restructuring and insolvency processes.
- Cross-Border Issues: Companies with global operations face the complexities of cross-border bankruptcy regulations, complicating reorganisation efforts. The necessity for coordination among different legal systems is paramount, particularly in restructuring and insolvency cases where assets and liabilities span multiple jurisdictions. Recent statistics indicate a rise in cross-border bankruptcy cases, underscoring the importance of strategic planning in global operations.
- Recent Developments: Staying informed about legislative changes is crucial for professionals engaged in reorganising. For example, 2024 marked the highest half-yearly corporate failures since H1 2018, signalling a critical need for effective restructuring strategies. This trend highlights the necessity for companies to engage in proactive planning and risk management to address issues related to restructuring and insolvency effectively. Additionally, anticipated reforms in personal bankruptcy frameworks, especially concerning digital assets, illustrate the evolving landscape of bankruptcy law. The UK Jurisdiction Taskforce’s focus on adapting to blockchain technology demonstrates the need for bankruptcy professionals to remain aware of technological innovations and their effects on legal practices.
- Case Studies: Examining global legal frameworks through case studies provides valuable insights. For instance, the anticipated changes in the treatment of Individual Voluntary Arrangements (IVAs) reflect the need for stricter adherence to industry standards, given the high failure rates observed. The case study titled “Future of Personal Insolvency and Digital Assets” highlights how organisations can navigate these challenges effectively. Such case studies not only emphasise jurisdictional variations but also offer practical examples of how companies can successfully manage financial difficulties.
- Expert Opinions: Engaging with expert perspectives on jurisdictional variations in restructuring and insolvency laws can further illuminate the complexities involved. As the landscape continues to change, professionals must adjust their strategies to align with the latest legal frameworks and market conditions, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle the complexities of restructuring and insolvency in 2025.
- Market Context: Additionally, the current weak demand for office space has prompted many owners to consider converting underutilised office assets into residential real estate. This trend presents unique reorganisation opportunities and challenges, particularly in the real estate sector, further emphasising the need for strategic planning in response to changing market dynamics.
Key Stakeholders in Restructuring and Insolvency: Roles and Responsibilities
In any restructuring or insolvency scenario, several key stakeholders play critical roles that significantly influence the outcome:
- Creditors: As the most influential stakeholders, creditors hold substantial power in the restructuring process. Their cooperation is essential for successful negotiations and the overall viability of the restructuring plan. Comprehending their rights, which encompass the ability to vote on proposed plans and to receive timely information about the debtor’s economic status, is crucial for all parties involved.
- Debtors: The distressed company must navigate its obligations to creditors while striving to regain economic stability. Debtors are responsible for providing clear financial information and participating in good faith discussions with creditors to create a viable plan that addresses their concerns and priorities related to restructuring and insolvency.
- Insolvency Practitioners: These professionals play a pivotal role in managing the process of restructuring and insolvency. They ensure adherence to legal obligations, facilitate negotiations among stakeholders, and offer expert advice on the best strategies for reorganisation. Their expertise is vital in balancing the interests of all parties and steering the process toward a successful resolution.
- Employees: Workers are directly affected by organisational changes, making their engagement and communication vital for maintaining morale and productivity. Effective communication strategies can help mitigate uncertainty and foster a supportive environment during transitions. Statistics indicate that organisational changes can lead to significant alterations in workforce dynamics, emphasising the need for careful consideration of employee rights and responsibilities throughout the process.
In 2025, the environment of corporate restructuring and insolvency continues to evolve, with creditors progressively asserting their rights in bankruptcy situations. Recent rulings have reinforced that state law cannot prevent a creditors’ committee from prosecuting claims on behalf of a bankruptcy estate, emphasising the role of creditors in the context of restructuring and insolvency processes. Furthermore, the effect of restructuring and insolvency on employees remains a critical consideration, as companies must balance financial recovery with the well-being of their workforce.
By emphasising teamwork and transparent communication among all parties, organisations can manage the challenges of reorganisation and financial distress more efficiently. Moreover, Naismiths’ differentiation through director-led instruction and a customer-centric approach serves as a real-world example of effective stakeholder engagement in transformation scenarios.
Best Practices for Successful Restructuring and Insolvency Management
To effectively manage reorganisation and insolvency, adopting the following best practices is essential:
- Early Engagement: Engaging key stakeholders at the outset is crucial for fostering collaboration and transparency. This proactive approach not only builds trust but also aligns interests, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes. Statistics indicate that organisations prioritising early stakeholder involvement see a marked improvement in success rates during changes, with some studies suggesting an increase of up to 30% in favourable outcomes. This aligns with Naismiths’ commitment to prioritising clients’ commercial interests while navigating sensitive situations.
- Clear Communication: Maintaining open lines of communication with all stakeholders is vital for managing expectations and alleviating uncertainty. Effective communication strategies can mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that all parties are informed of developments, which is particularly important in times of organisational change. Research indicates that companies with strong communication frameworks during organisational changes experience 25% less resistance from employees. Moreover, with 32% of employers citing employee retention as a primary hiring issue, focusing on communication can enhance employee satisfaction and engagement, which is critical during organisational changes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leveraging analytics and forecasting tools is essential for informing strategies and assessing potential outcomes. By utilising advanced data analytics, organisations can make informed decisions grounded in empirical evidence, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of their organisational changes. This approach not only aids in identifying risks but also in optimising resource allocation. Naismiths Analytics exemplifies this by providing advanced cost forecasting tools, interactive dashboards, and bespoke reports that enhance decision-making, offering accurate cost data and risk management solutions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The ability to adjust strategies in response to evolving circumstances and stakeholder feedback is critical. The processes of restructuring and insolvency are rarely linear; thus, organisations must remain agile and responsive to changes in the market or internal dynamics. This adaptability can result in more innovative solutions and enhanced stakeholder satisfaction.
- Post-Change Monitoring: Implementing a robust monitoring system is essential for tracking the effectiveness of change initiatives. Ongoing evaluation enables organisations to make necessary adjustments and ensures that objectives are being met. This ongoing evaluation is key to sustaining improvements and achieving long-term success in the aftermath of organisational changes.
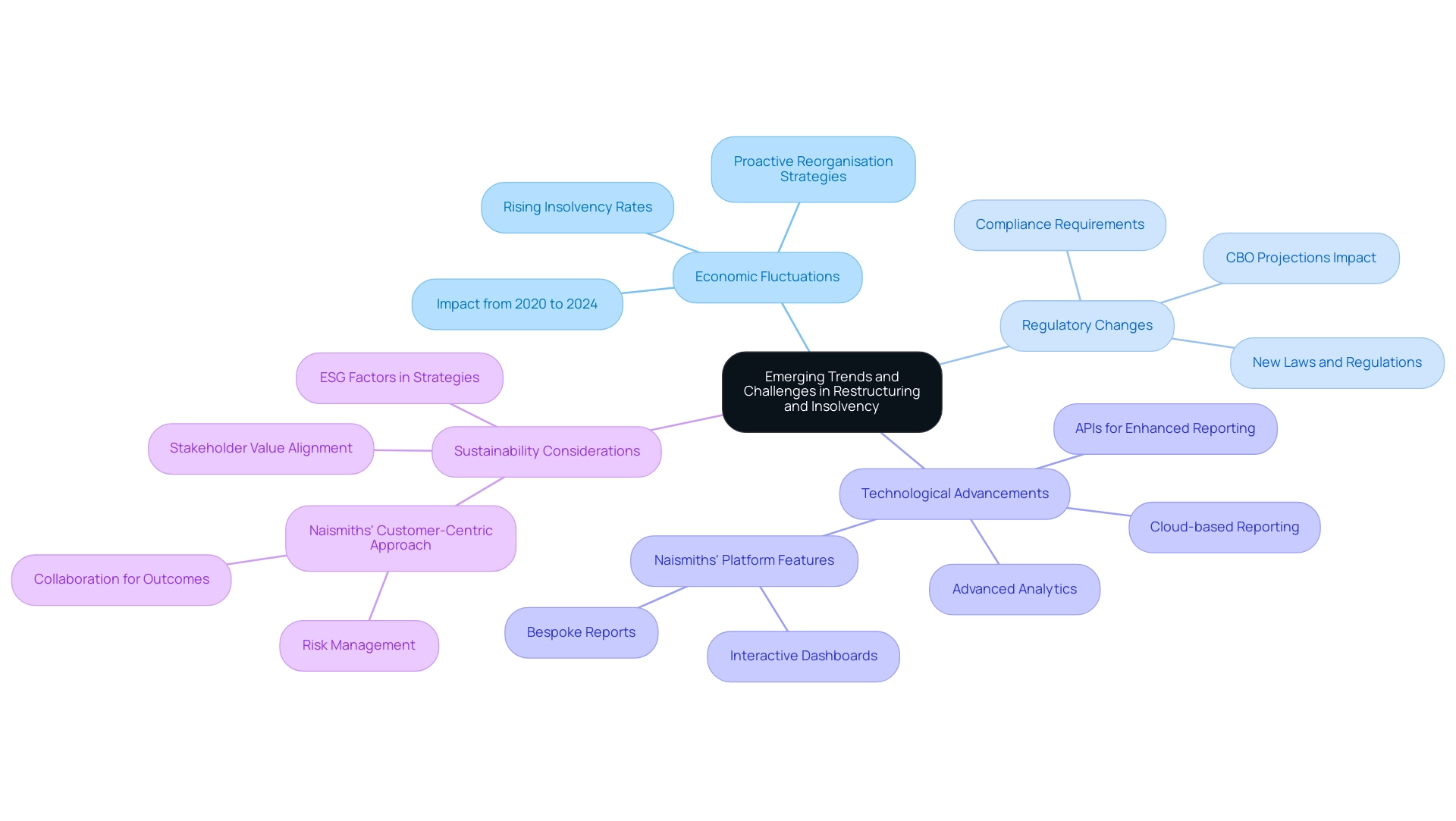
Emerging Trends and Challenges in Restructuring and Insolvency
As the landscape of reorganisation and insolvency continues to evolve, professionals must navigate several key trends and challenges:
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic instability directly correlates with rising insolvency rates. Recent data indicates that fluctuations in economic performance have led to a notable increase in business filings, with a significant rise observed from 2020 to 2024. This underscores the necessity for proactive reorganisation strategies that can adapt to changing market conditions. Firms must adopt effective measures to address this trend.
- Regulatory Changes: The introduction of new laws and regulations significantly impacts restructuring and insolvency processes. Staying informed about these legal developments is crucial for professionals aiming to implement effective strategies. In 2025, anticipated regulatory adjustments will further influence reorganisation statistics, necessitating a keen awareness of compliance requirements.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology into reorganisation practices is transforming operations. Advanced analytics and forecasting tools enhance decision-making capabilities, allowing firms to respond swiftly to economic challenges. This technological shift streamlines processes and improves the accuracy of financial assessments. Naismiths’ platform exemplifies this advancement, offering an intuitive interface for users to input and track key data for property development projects. With secure, cloud-based SQL database storage, it facilitates clear, standardised reporting and analysis, essential for investment fund managers navigating complex transformation scenarios. Additionally, the platform features interactive dashboards and bespoke reports that provide tailored insights, while application programming interfaces (APIs) pull in information from external data sources to enhance reporting capabilities.
- Sustainability Considerations: There is an increasing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors within reorganisation strategies. Companies are now more focused on aligning their operations with stakeholder values, reshaping their approach to organisational changes. This trend reflects a broader commitment to sustainable practices, influencing both corporate strategy and investor expectations. Naismiths exemplifies a unique approach in this evolving landscape. In summary, understanding these dynamics is essential for professionals in the field as they navigate the complexities of restructuring and insolvency in an ever-changing economic landscape.
Conclusion
Restructuring and insolvency represent critical processes that demand a comprehensive understanding of their complexities and implications. This article underscores the significance of early engagement with stakeholders, clear communication, and data-driven decision-making as essential components for successful restructuring efforts. The roles of key stakeholders—creditors, debtors, insolvency practitioners, and employees—illustrate the collaborative nature of the restructuring process, where each party plays a vital role in steering the organisation toward recovery.
As the economic landscape continues to fluctuate, the necessity for adaptive and flexible strategies becomes increasingly paramount. Professionals must remain vigilant in staying informed about regulatory changes and technological advancements that can significantly impact restructuring and insolvency practices. Moreover, the incorporation of sustainability considerations into restructuring strategies reflects a shift in corporate responsibility and stakeholder expectations, further complicating the landscape.
Ultimately, navigating the intricacies of restructuring and insolvency necessitates a proactive approach that prioritizes collaboration, communication, and continuous adaptation. By embracing best practices and emerging trends, organisations can enhance their resilience and improve their chances of achieving sustainable recovery in a challenging economic environment. The future of financial recovery lies in the ability to effectively manage these processes while fostering strong relationships among all stakeholders involved.